Decisions, decisions, decisions…. RFID vs Barcode can be a challenging process to determine which is best for your organization as there are many benefits of both. Each set of technologies has it’s own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will list the advantages of each and help you decide which technology is right for you fixed asset tracking project.
Hint: Maybe it’s a combination of both 😉
What is RFID?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), is a data collection technology that allows you to collect data via a radio frequency wave. There are 3 main components of an RFID system:
- RFID Tags
- RFID compatible reader
- Grey Trunk Software
RFID tags are placed on the assets and are programmed with a unique serial number. In most cases, an passive UHF RFID tag is used. The reader then powers the tag to transmit a radio wave to collect the data. The data from the tag is stored in a database and the RFID software then makes sense of that data to display to the user.
What is a Barcode?
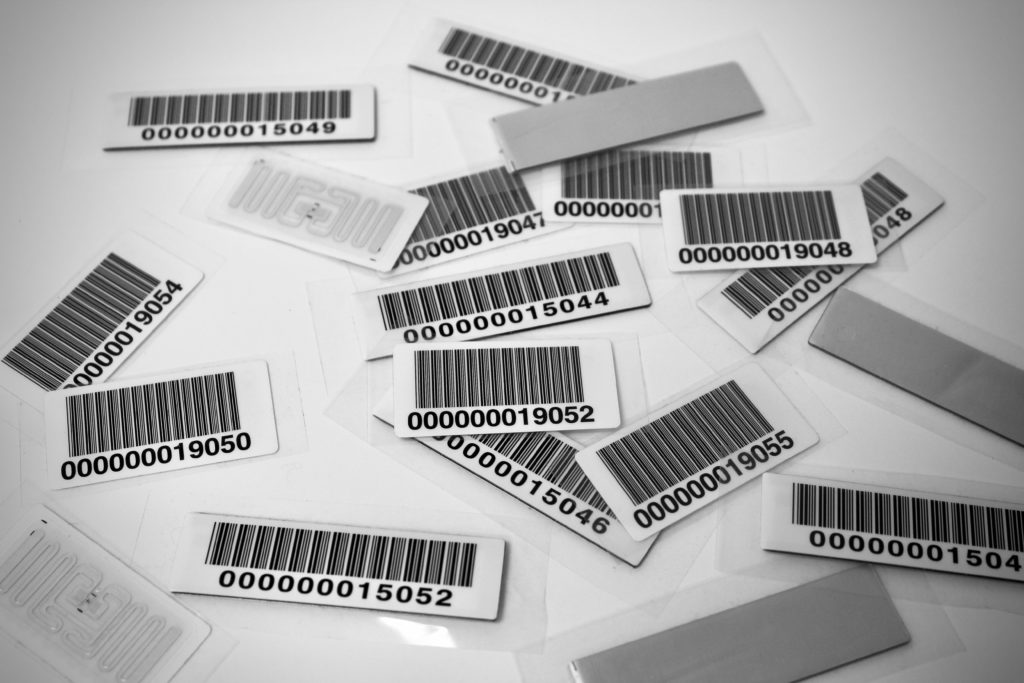

The technical definition for a barcode is a machine-readable form of information on a scannable, visual surface. A barcode consists of bars and spaces of varying width that can be read with an optical barcode scanner. This is another way to capture data. The user scans the barcode to collect the serial number and then stores it in a database.
Many of you will correlate the barcode with a UPC code found on packaging. Think of the grocery store or supermarket when you check out.
Barcodes have been around since 1974 when the Wrigley gum company put a barcode on their gum package and changed the supermarket industry forever — see the history of the barcode here.
RFID vs. Barcode | Advantages for Asset Tracking
Advantages of RFID:
- No line of sight required for the tag
- Long read ranges – up to 30-40 feet in some scenarios.
- Readers can scan multiple tags at once
- Reduce inventory time
- Tags can use both RFID and Barcode, such as these from Metalcraft.
- No data entry errors
- Improved efficiency for entering data
- Barcode tags are inexpensive
- Minimal hardware costs
HINT: There are no hardware costs if you use a mobile asset tracking system — your mobile device’s camera can scan barcodes.
RFID vs Barcode | Disadvantages for Asset Tracking
Disadvantages of RFID:
- Requires higher investment than barcode
- Surface dependent — liquids and metals can affect read range of tags
Disadvantages of Barcode:
- Line of sight required for each asset
- Very close read range
- Barcodes could become damaged, scuffed, or scratched
TIP: Here are 5 Tips for Choosing the Perfect Asset Tracking Software
Conclusion
When we break it down, there are a lot of benefits to using both barcode and RFID technologies in the same tag. It all starts with the tag for data collection of the fixed asset. In some cases, RFID works very well, specifically for fixed asset inventories. In other cases, barcodes make the most sense.
Why use both technologies?
- There is a minimal additional investment to add the barcode to the RFID tag.
- If you are tracking mobile assets that move between facilities, not all locations may be equipped to support reading RFID so having the barcode as a redundant technology allows the tag to be read with a scanner.
- Having the barcode information programmed into the RFID chip provides reassurance and data redundancy.
- Most asset tracking software, such as Grey Trunk RFID, is capable of using both barcode and RFID.
If you need to learn more about RFID vs Barcode and see for yourself which technology will work best for your organization, schedule a 30 minute live demo so you can see Grey Trunk RFID in action.